I had a challenge with a freezer getting unplugged a few weeks ago, luckily, I had caught it before everything got above 40 (refrigerator temperature), so the food was not spoiled but instead cooked in quick order.
I had worked with ESP8266 and arduino before, but my old ESP8266 boards were no longer working. (my friend had given them to me, they were clones, and, had a high failure rate.) So I ordered a ESP32.
What I wanted to do was take what I had been working on with serverless cloud architectures, and see if this could solve some limitations of arduino IDE only implementations, such as, updating logic complexity, getting email notifications, and web access. After doing this the first time, and replicating it to the garage door sensor, I end up with a fungible building block to be able to use ESP as a sensor and have both cloud based notifications, as well as remote validation on mobile, for whatever solution is needed.
The solution created is novel for a few approaches,
- Uses AWS free tier.
- Is completely serverless and decoupled.
- Has the more complex logic in cloud, it doesn’t need changes to ESP
- The ESP is simple, it reads temperature every 10 minutes and at startup, and sends a temperature alert to AWS API gateway.
- When the temperature exceeds a limit, it will send a notification to email. It could also go to SMS, but this is not in the free tier.
- It can be checked from any browser, anywhere, at a standard URL
I have done a similar build for my garage door, with the key difference being it measures door state, and will send an update at 10pm if my garage door is open.
I googled the pinouts from here, https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-ds18b20-temperature-arduino-ide/ or similar connections, I annotate it below but this is important. At the early stages you should be able to validate that you are sending the temperature/door state, and getting a response from API Gateway. If this works, the rest of the work is in the cloud.
While I had done most of this before, the lamda code and frontend was vibe coded using antigravity. The only functional difference in the drawing below is I don’t measure freezer temperature over time, although I could, I have no reason to today. That is a future development plan, of extremely low priority. The nice thing about this is there would not need to be any changes to ESP32, it would all be backend.
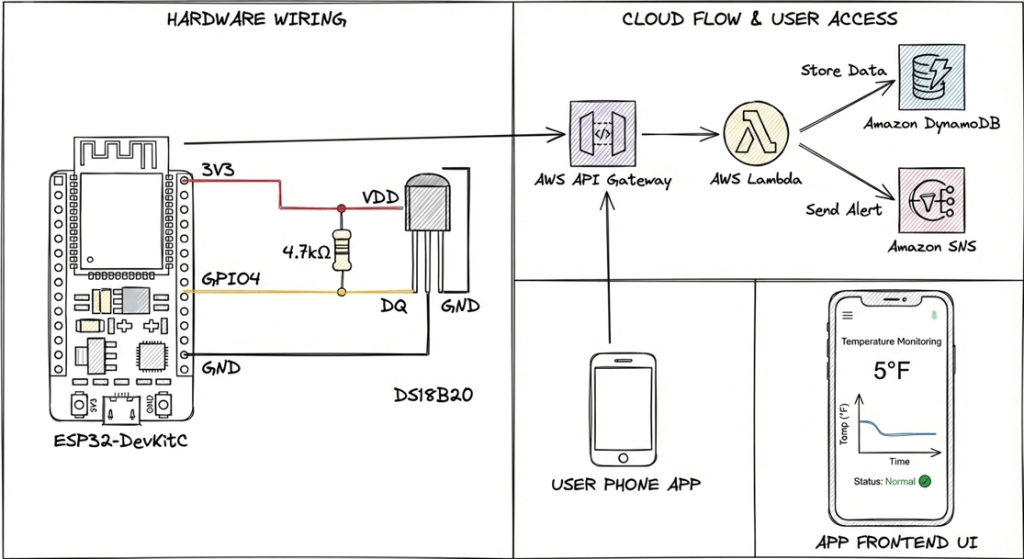
Sequencing
I like to see incremental progress, so I chose to setup API gateway and Lambda and DynamoDB, then the ESP. I then enabled SNS.
You need to have the API configured for the ESP32 to send to. You could,
- Setup ESP32 and validate it is working (reading temp) from console monitor, then reflash when you setup API Gateway and backend.
- Setup full backend then Setup ESP
- Do a hybrid like I did with a API gateway setup then incrementally adding backend.
ESP 32
I do use wifimanager instead of hardcoding Wifi, in case I need to move it in the future.
A more optimal longer term solution for many of these, would be to decouple the URL with DNS, so that instead of hardcoding “aws-api-information.aws.com” I could use freezermon.strongedge.io and change DNS to redirect if my API gateway were to change in the future.
The issue here being I prefer the obfuscation of the AWS API, I don’t care to have my information able to be reverse engineered.
#include <WiFiManager.h> // https://github.com/tzapu/WiFiManager#include <OneWire.h>#include <DallasTemperature.h>#include <HTTPClient.h>#include <WiFiClientSecure.h>#include <ArduinoJson.h>// -------------------------------------------------------------------------// CONFIGURATION// -------------------------------------------------------------------------// Pin Configuration#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 4 // GPIO pin for DS18B20 data line#define LED_PIN 2 // Onboard LED (usually GPIO 2 on ESP32 DevKit)// API Configuration - UPDATE THESE WITH YOUR VALUES#define API_ENDPOINT "https://your-api-id.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod/temperature" #define API_KEY "your-api-key-here"#define DEVICE_ID "freezer_monitor_01"// Timing Configuration#define READING_INTERVAL_MS 600000 // 10 minutes in milliseconds// -------------------------------------------------------------------------// GLOBALS & OBJECTS// -------------------------------------------------------------------------OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire);WiFiManager wifiManager;unsigned long lastReadingTime = 0;bool initialReading = true;// LED Status Patternsenum LedState { LED_OFF, LED_SOLID_ON, LED_SLOW_BLINK, // 1s on/off LED_RAPID_BLINK // 0.2s on/off};LedState currentLedState = LED_SOLID_ON;// -------------------------------------------------------------------------// HELPER FUNCTIONS// -------------------------------------------------------------------------void setLedState(LedState state) { currentLedState = state;}void updateLed() { unsigned long currentMillis = millis(); switch (currentLedState) { case LED_OFF: digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); break; case LED_SOLID_ON: digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); break; case LED_SLOW_BLINK: if ((currentMillis / 1000) % 2 == 0) digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); else digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); break; case LED_RAPID_BLINK: if ((currentMillis / 200) % 2 == 0) digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); else digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); break; }}// Flash LED rapidly for a set duration (blocking) to indicate errorvoid flashErrorLed() { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); delay(100); digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); delay(100); }}float readTemperature() { Serial.println("Requesting temperatures..."); sensors.requestTemperatures(); float tempF = sensors.getTempFByIndex(0); if (tempF == DEVICE_DISCONNECTED_F) { Serial.println("Error: Could not read temperature data"); return -999.0; } Serial.print("Temperature: "); Serial.print(tempF); Serial.println(" F"); return tempF;}bool sendDataToAWS(float tempF) { if (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { Serial.println("Error: WiFi not connected"); return false; } WiFiClientSecure client; client.setInsecure(); // Skip certificate verification for simplicity in V1 HTTPClient http; Serial.print("Connecting to endpoint: "); Serial.println(API_ENDPOINT); if (!http.begin(client, API_ENDPOINT)) { Serial.println("Error: Failed to begin HTTP connection"); return false; } http.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json"); http.addHeader("x-api-key", API_KEY); // Create JSON payload StaticJsonDocument<200> doc; doc["device_id"] = DEVICE_ID; doc["temperature_f"] = tempF; // We don't send timestamp from device as it might have drifted/no RTC. // Ideally backend adds timestamp, but PRD 3.3 shows it in JSON. // We'll use a placeholder or 0 if no NTP, or let Lambda handle it. // However, PRD 3.3 example shows "timestamp": 1705234567. // Let's omit it for V1 simplicity or add it if we had NTP. // The schema says V1 uses sort key 0 for current reading in DynamoDB, // but Lambda logic likely adds timestamp if missing or uses current time. // We will assume Lambda adds it for now to keep device code simple as per "No additional infrastructure" String requestBody; serializeJson(doc, requestBody); Serial.println("Posting data: " + requestBody); int httpResponseCode = http.POST(requestBody); bool success = false; if (httpResponseCode > 0) { Serial.print("HTTP Response value: "); Serial.println(httpResponseCode); String response = http.getString(); Serial.println(response); if (httpResponseCode == 200) { success = true; } } else { Serial.print("Error code: "); Serial.println(httpResponseCode); } http.end(); return success;}// -------------------------------------------------------------------------// SETUP// -------------------------------------------------------------------------void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); // Start with LED OFF digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); Serial.println("\nStarting Freezer Monitor..."); // Initialize Sensors sensors.begin(); // WiFi Manager // Local intialization. Once its business is done, there is no need to keep it around WiFiManager wifiManager; // Reset settings - for testing // wifiManager.resetSettings(); // Set timeout wifiManager.setConfigPortalTimeout(180); // 3 minutes timeout // Connect or start AP if (!wifiManager.autoConnect("ESP32-Setup")) { Serial.println("Failed to connect and hit timeout"); delay(3000); //reset and try again, or maybe put it to deep sleep ESP.restart(); delay(5000); } // If you get here you have connected to the WiFi Serial.println("Connected to WiFi!"); setLedState(LED_SOLID_ON);}// -------------------------------------------------------------------------// MAIN LOOP// -------------------------------------------------------------------------void loop() { // Update LED status (non-blocking mostly, but helper loop) updateLed(); unsigned long currentMillis = millis(); // Check if it's time to read (every 10 minutes) if (initialReading || (currentMillis - lastReadingTime >= READING_INTERVAL_MS)) { Serial.println("--- Starting Measurement Cycle ---"); // Status: Reading setLedState(LED_SLOW_BLINK); // Maintain LED blink while doing work (blocking calls might interrupt this simple loop, // but we can call updateLed() inside long operations if needed, or use tasks. // For V1 simple loop is fine, blink might pause during HTTP call). float temp = readTemperature(); if (temp != -999.0) { bool sent = false; int retries = 0; while (!sent && retries < 3) { updateLed(); // Keep LED alive if (sendDataToAWS(temp)) { sent = true; Serial.println("Data sent successfully."); } else { Serial.println("Failed to send data. Retrying..."); retries++; setLedState(LED_RAPID_BLINK); // Exponential backoff: 1s, 2s, 4s unsigned long wait = 1000 * (1 << (retries - 1)); delay(wait); } } if (!sent) { Serial.println("Failed sending after 3 retries."); flashErrorLed(); } } else { Serial.println("Skipping upload due to sensor error."); flashErrorLed(); } lastReadingTime = currentMillis; initialReading = false; Serial.println("--- Cycle Complete. Waiting... ---"); setLedState(LED_SOLID_ON); } // Simple check for WiFi connection if (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) { setLedState(LED_OFF); // Or rapid blink to indicate lost connection? PRD says Rapid blink = API error, Off = not powered. // Let's just try to reconnect silently or let WiFiManager handle it? // WiFiManager is blocking during config, but we are in loop. // Reconnection is usually auto-handled by ESP32, but we can force it. // Logic: "WiFi reconnection attempts if connection lost" // We'll leave it to background task or simple check. }}API Gateway
- Create REST API.
- Resource:
/temperature(POST) -> Integration: Lambda Function. - Resource:
/temperature/current(GET) -> Integration: Lambda Function.- Note: Ensure
Use Lambda Proxy integrationis checked for both of these - You dont need the API key set to the Get method. You do on the POST.
- This is because we dont want to expose API key in the Javascript code, needed on the browser, so we leave the Get method unkeyed.
- Note: Ensure
- Enable CORS. I believe i did this on POST and GET. It was definately required.
- Create API Key and Usage Plan. You need to setup a usage plan for to enable API key.
- Deploy API to Stage
prod.
SNS
- Create Topic:
freezer-temperature-alerts - Create Subscription: Email (confirm via email).
- Copy Topic ARN. #
Lamda
- Create function:
freezer-temperature-processor(Python 3.x) - Add Environment Variables:
MAX_TEMP_F:10SNS_TOPIC_ARN: (Your Topic ARN)DYNAMODB_TABLE:freezer-temperatures
- Grant IAM permissions:
dynamodb:PutItem,dynamodb:GetItem,sns:Publish.
import jsonimport osimport timeimport boto3from decimal import Decimalfrom botocore.exceptions import ClientError# Initialize AWS clientsdynamodb = boto3.resource('dynamodb')sns = boto3.client('sns')# Configuration from Environment VariablesTABLE_NAME = os.environ.get('DYNAMODB_TABLE', 'freezer-temperatures')SNS_TOPIC_ARN = os.environ.get('SNS_TOPIC_ARN')MAX_TEMP_F = os.environ.get('MAX_TEMP_F', '10') # Default 10FMIN_TEMP_F = os.environ.get('MIN_TEMP_F', '') # Default emptydef decimal_default(obj): if isinstance(obj, Decimal): return float(obj) raise TypeErrordef get_current_time(): return int(time.time())def send_alert(device_id, temp_f, threshold, is_min_violation=False): if not SNS_TOPIC_ARN: print("Error: SNS_TOPIC_ARN not set") return violation_type = "Low" if is_min_violation else "High" limit_val = MIN_TEMP_F if is_min_violation else MAX_TEMP_F subject = f"⚠️ Freezer Temperature Alert: {temp_f}°F" message = ( f"Your freezer temperature is out of safe range:\n" f"- Current Temperature: {temp_f}°F\n" f"- {violation_type} Limit: {limit_val}°F\n" f"- Device: {device_id}\n" f"- Time: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.gmtime())} UTC" ) try: sns.publish( TopicArn=SNS_TOPIC_ARN, Subject=subject, Message=message ) print(f"Alert sent for {device_id}") except ClientError as e: print(f"Error sending SNS: {e}")def lambda_handler(event, context): print("Received event:", json.dumps(event)) table = dynamodb.Table(TABLE_NAME) method = event.get('httpMethod') # ------------------------------------------------------------------ # GET: Retrieve current temperature # ------------------------------------------------------------------ if method == 'GET': # For V1 we assume single device or query param. # PRD doesn't specify how to select device in GET, defaulting to 'freezer_monitor_01' # or checking query parameters. device_id = "freezer_monitor_01" qs = event.get('queryStringParameters') if qs and qs.get('device_id'): device_id = qs.get('device_id') try: response = table.get_item( Key={ 'device_id': device_id, 'timestamp': 0 # V1 Design: fixed sort key 0 } ) item = response.get('Item') if item: return { 'statusCode': 200, 'headers': { 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*', 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers': 'Content-Type,x-api-key', 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'OPTIONS,POST,GET' }, 'body': json.dumps(item, default=decimal_default) } else: return { 'statusCode': 404, 'headers': {'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'}, 'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Device not found'}) } except ClientError as e: print(e) return { 'statusCode': 500, 'headers': {'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*'}, 'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Internal Server Error'}) } # ------------------------------------------------------------------ # POST: Ingres new reading # ------------------------------------------------------------------ if method == 'POST': try: body = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}')) device_id = body.get('device_id') temp_f = float(body.get('temperature_f')) # We enforce timestamp here current_ts = get_current_time() if not device_id or temp_f is None: return { 'statusCode': 400, 'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Missing device_id or temperature_f'}) } # Check logic alert_needed = False is_min = False # Check Max if MAX_TEMP_F and temp_f > float(MAX_TEMP_F): alert_needed = True # Check Min if MIN_TEMP_F and temp_f < float(MIN_TEMP_F): alert_needed = True is_min = True # Retrieve existing state for alert deduplication existing_item = {} try: resp = table.get_item(Key={'device_id': device_id, 'timestamp': 0}) existing_item = resp.get('Item', {}) except ClientError: pass # Proceed as if new last_alert = existing_item.get('last_alert_timestamp', 0) last_alert_val = int(last_alert) if last_alert else 0 new_last_alert = last_alert_val if alert_needed: # Check 1 hour cooldown (3600 seconds) if (current_ts - last_alert_val) > 3600: send_alert(device_id, temp_f, MAX_TEMP_F if not is_min else MIN_TEMP_F, is_min) new_last_alert = current_ts else: print("Alert condition suppressed (cooldown active)") else: # Optional: Reset alert timestamp if back to normal? # PRD doesn't specify, but usually we don't need to reset cooldown if normal. pass # Update DynamoDB # V1 Design: Overwrite Sort Key 0 item = { 'device_id': device_id, 'timestamp': 0, 'temperature_f': Decimal(str(temp_f)), 'last_updated': current_ts, 'last_alert_timestamp': new_last_alert } table.put_item(Item=item) return { 'statusCode': 200, 'body': json.dumps({'message': 'Data received', 'temperature': temp_f}) } except Exception as e: print(f"Error processing POST: {str(e)}") return { 'statusCode': 500, 'body': json.dumps({'error': str(e)}) } return { 'statusCode': 400, 'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Unsupported method'}) }DynamoDB
- Create table:
freezer-temperatures - Partition Key:
device_id(String) - Sort Key:
timestamp(Number)
S3 static website frontend
This was the area that I was least familiar with. It is also very verbose…
I knew I wanted a static website hosted on S3 in the free tier. I fed my parameters in and vibe coded it. I recommend you do the same, the parameters were
- read Temperature/door state from API Gateway using created API URL
- display
- run on S3 free tier.
Of note on this, you need to enable S3 website hosting, after you upload the files. The website itself is very straightforward, and the javascript runs in the browser and does the API call.
Troubleshooting and conclusion
Troubleshooting is part of the fun in learning some AWS Nuance. If you are sending your temperature alerts, you can see that in ESP32 console. If you are getting a response, you can use that.
Cloudwatch logs is where you will troubleshoot. It will tell you what the issue is. A note is the API Gateway will not log by default, which is fine. If you are getting 500 errors, it is something between API GW and Lambda. Probably a CORS item. Any other items can be googled, but pay attention to IAM if you do any changes (i changed dynamoDB table name during troubleshooting and had to update IAM).
Overall this was a fun and useful fungible building block to take ESP as a decoupled sensor, whether using a reed sensor, temperature sensor, or any other monitoring, and take the framework and create a serverless cloud based infrastructure to enable notifications and web access.